Automotive PCBA Manufacturing
Mission-Critical Automotive Electronics Built for Extreme Conditions Our automotive PCBA manufacturing meets IATF 16949 and AEC-Q100 standards, delivering uncompromising reliability for vehicle systems. From engine control units to ADAS sensors, we design and assemble boards that withstand temperature extremes (-40°C to 125°C), vibration, and moisture while maintaining signal integrity. With 100% automated optical inspection (AOI) and functional testing, we ensure zero-defect performance in safety-critical applications where failure is not an option.
Next-Gen Vehicle Electronics ManufacturingAs vehicles evolve into connected, autonomous platforms, our PCBA solutions power the transition. We specialize in high-density interconnect (HDI) designs for compact EV battery management systems, robust flex PCBs for in-cabin displays, and high-speed boards for LiDAR/radar modules. Our manufacturing processes incorporate automotive-grade components with PPAP documentation and full traceability, future-proofing your designs against evolving ISO 26262 functional safety requirements.
- IATF 16949-certified production
- Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) experience
- AEC-Q100 qualified components
- Vibration/shock-resistant designs for electric vehicles
Powering the next generation of electric mobility, we engineer high-voltage PCB assemblies (up to 1000V) specifically for EV applications. Our solutions integrate advanced materials and layout techniques to meet critical safety requirements, including reinforced 8mm+ creepage distances, CTI-600 rated substrates, and liquid-cooled thermal management for high-current applications. Specializing in battery management systems (BMS), onboard chargers, and traction inverters, we combine automotive-grade reliability (AEC-Q100 components, ISO 26262 processes) with scalable manufacturing to support OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers. Our value-engineered designs optimize for both performance and cost—utilizing simulation-driven DFM to reduce layer counts while maintaining 175°C+ temperature resilience for harsh under-hood environments.
Importance of Automotive PCB
As autonomous driving technology and the concept of new energy vehicles continue to rise, the automotive PCB market is expanding and moving towards the high end.
Automotive PCB Applications
Automobiles have transformed simple mechanical machines into highly complex electronic systems, and this transformation is inseparable from the close integration of PCB technology. With the continuous development of HDI technology and miniaturized SMD components, PCBA boards appear in various corners of automobiles in smaller and more intricate forms. As the central nervous system of automotive electronic systems, PCB facilitates communication and control between various components, meeting the specific customization needs of automobile manufacturers. Examples of some automotive PCB applications include:
- ECM: Modern cars have moved away from traditional engine configurations and now rely on PCB as the core of ECM systems to optimize engine performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions, driving the automotive industry toward a cleaner and more efficient direction.
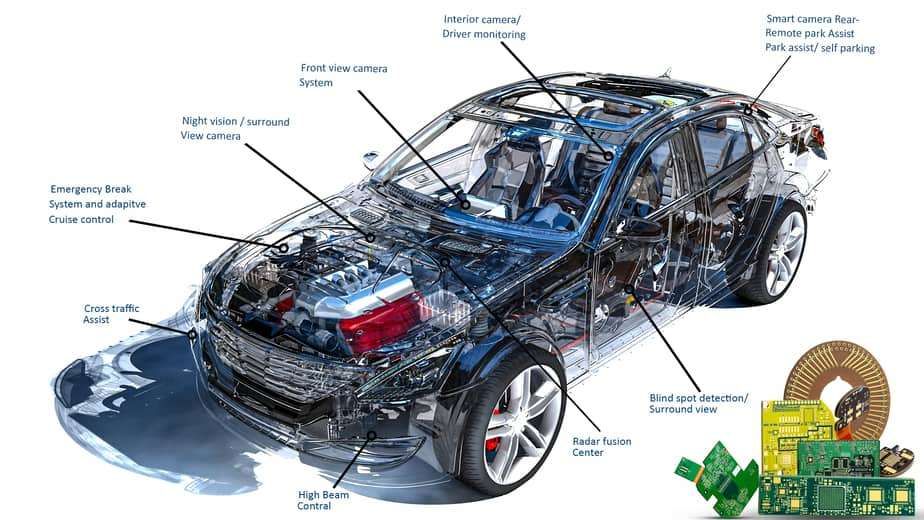
- Safety systems: Safety systems include features like full airbag deployment, collision detection, and anti-lock braking systems, demanding high reliability and precision. They must respond quickly when drivers face danger to ensure passenger safety.
- Infotainment systems: In-vehicle infotainment systems provide entertainment and connectivity for passengers, and our PCB plays a crucial role in the seamless operation of touchscreens, audio systems, and navigation devices, enhancing the driving experience.
- BMS: With the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), BMS PCBs have become crucial. These PCBs are used to manage and monitor the performance and health of electric vehicle batteries to ensure safety and longevity.
- ADAS: Features such as lane-keeping assistance and adaptive cruise control rely on PCB for real-time data processing, improving vehicle safety and providing more support and protection to drivers.
Automotive PCB Market
Some data from the automotive industry is given below:
| Industry | Automotive Electronics |
|---|---|
| Growth Projection (CAGR 2022-2027) | Over 7% |
| Market Size (Projected 2027) | Approximately $500 billion |
| Key Drivers | — Electric Vehicles — Autonomous Driving Systems — Advanced Safety Features — In-Car Infotainment |
| Impact on PCB | Increasing demand for high-end PCB |
| Industry Influence on Automotive Sector | Reshaping the future of the automotive industry |
The global automotive motors market was valued at USD 28 billion in 2022, and it is projected to increase to around USD 42.86 billion by 2032. This growth is expected to occur at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 4.4% during the forecast period from 2023 to 2032.
Automotive PCB Design Guide
The variety of automotive systems demands a wide range of PCB types. Even within the same vehicle, selecting the appropriate PCB based on system requirements is a crucial aspect to ensure the smooth progress of your project.
As electronic components drive the increase in automotive parts and features, the demand for various types of PCB in cars is only set to rise. Automotive PCB manufacturers need to provide a wide range of PCB options. Today, printed circuit boards are used to enhance efficiency and safety in various systems and operations, including head and tail LED lights, gearbox control, and comfort control units. You can also find automotive PCBs used in the management of engines, entertainment systems, digital displays, radar, GPS, power relay timing systems, rearview mirror control, and more.
| Aspect | Automotive PCB | Normal PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Component Durability | Designed for robustness and durability to withstand automotive conditions, such as vibrations and temperature variations. | May not have the same level of durability, as they are not exposed to the same environmental stresses. |
| Extended Temperature Range | Must operate effectively across a wide temperature range often found in automotive environments. | Designed for standard temperature ranges and may not have the same extended temperature tolerance. |
| Vibration and Shock Resistance | Built to endure constant vibrations and shocks associated with vehicle movement. | Typically not engineered with the same level of vibration and shock resistance. |
| EMI/RFI Shielding | Require effective shielding to protect sensitive electronics from electromagnetic and radio-frequency interference. | May not have the same level of EMI/RFI shielding. |
| Compliance with Automotive Standards | Must adhere to specific automotive safety and quality standards. | May not be subject to the same automotive industry standards. |
Temperature Extremes
The automotive industry faces a wide range of temperature challenges, with vehicles operating in both extremely hot and cold environments. These temperature extremes can significantly impact the reliability and performance of PCB. Notable examples include the under-hood temperatures in internal combustion engine vehicles and the extreme cold in electric vehicles in northern regions.
Design Solution: To address these temperature challenges in automotive PCB design, it’s essential to start by selecting materials with high glass transition temperature (Tg) values to ensure stability. Strategically implement thermal vias to efficiently dissipate heat, particularly around power components. Consider the temperature profiles within the vehicle’s environment and adjust the layout accordingly. Utilize thermal simulations and conduct thermal cycling tests to validate your design’s performance.
Vibration and Mechanical Stress:
Vehicles are subject to various levels of vibration and mechanical stress during operation, which can result in solder joint fatigue and other mechanical failures in PCB.
Design Solution: To protect PCB from the challenges posed by vibrations and mechanical stress, it’s essential to prioritize the securement of components through mechanical design solutions such as shock mounts and grommets. Utilize vibration-resistant materials in areas prone to mechanical strain and reinforce the PCB’s structure for enhanced durability. Additionally, it’s crucial to perform comprehensive shock and vibration testing during the design phase to pinpoint vulnerabilities and ensure that your PCB can endure the rigorous conditions of the automotive environment.
Moisture, Chemical and Contaminant Resistance
PCB in vehicles are subjected to moisture, chemicals, and contaminants stemming from road conditions, weather, and maintenance chemicals such as engine fluids and cleaning agents.
Design Solution: To safeguard your PCB against the risks posed by moisture, chemicals, and contaminants, it is advisable to integrate features like conformal coatings, gaskets, and seals into your design. Opt for materials with robust chemical resistance to endure exposure to automotive fluids and cleaning agents effectively. Moreover, implement drainage and venting strategies to prevent the accumulation of moisture, and take the ingress protection (IP) rating into account when designing enclosures. By incorporating these measures, your PCB will maintain their resilience and reliability when confronted with the challenging conditions of the automotive environment.



